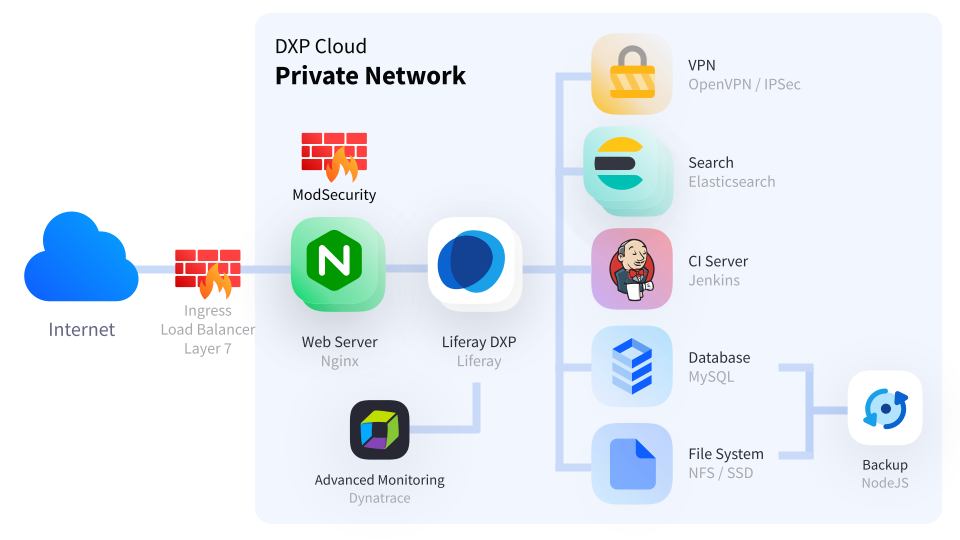
Web Application Firewall
Liferay Cloud 5.x.x
Liferay Cloud includes a web application firewall called ModSecurity. It inspects requests sent to the web server against a predefined set of custom rules. This step prevents typical web application real time L7 attacks, like XSS, SQL Injection, and other forms of hijacking attempts that might lead to loss of sensitive information.
Liferay Cloud includes additional network security features, including a private network, public load balancer (Layer 7), and CDN.
Custom firewall rules are not available with shared cluster subscriptions.
Enabling ModSecurity
ModSecurity is disabled by default. To enable it, add the LCP_WEBSERVER_MODSECURITY environment variable to your project repository’s webserver/LCP.json file. Attack detection rules are only processed if ModSecurity is enabled. You must add your own rules.
These values are allowed for LCP_WEBSERVER_MODSECURITY:
-
On: enables ModSecurity. Attack detection rules are processed.
-
Off: disables ModSecurity. Rules are not processed.
-
DetectionOnly: enables ModSecurity. Rules are processed, but disruptive actions are not executed (block, deny, drop, allow, proxy, or redirect).
The LCP_WEBSERVER_MODSECURITY environment variable is equivalent to ModSecurity’s own SecRuleEngine directive.
To enable ModSecurity, set the value of LCP_WEBSERVER_MODSECURITY to On or DetectionOnly, then deploy the change.
Changing ModSecurity’s Configuration
The default ModSecurity settings are recommended. To override the default configuration, create a modsecurity.conf file in your project repository’s webserver/configs/[ENV]/modsec/ directory. You must provide all necessary configurations, because it completely overrides Liferay Cloud’s default modsecurity.conf.
Copy this example of recommended settings as a starting point for your own modsecurity.conf file. If you use this file, replace the line SecRuleEngine DetectionOnly with this line:
SecRuleEngine ${LCP_WEBSERVER_MODSECURITY}
See the ModSecurity Reference Manual for more information on the allowed settings.
Adding Attack Detection Rules
Attack detection rules are not provided by default. You must provide rules according to your specific needs.
Some sets of rules might require Liferay DXP to be recompiled with them. To do this, you must make the necessary changes to the Liferay service and restart it.
Using ModSecurity Audit Logs
When enabled, ModSecurity automatically generates audit logs, recording detailed information for all transactions. To view the logged information, open the modsec_audit.log file in your web server’s /var/log directory.
If you configure ModSecurity by providing your own modsecurity.conf file, you can log the information in the web server’s console (where you can download it) instead of modsec_audit.log. Change this line in your modsecurity.conf file:
SecAuditLog /var/log/modsec_audit.log
Replace /var/log/modsec_audit.log with /dev/stdout to print audit logs for each transaction in the console. The audit logs appear once you deploy the change.
If desired, change the audit log format to JSON by adding one line to the modsecurity.conf file:
SecAuditLogFormat JSON