User Account API Basics
You can add and manage users from the Control Panel, but you can also use Liferay’s REST APIs. You can call these services to add, edit, delete users.
Start with adding a new user.
Adding Users
Start a new Liferay instance by running
docker run -it -m 8g -p 8080:8080 liferay/portal:7.4.3.120-ga120
Sign in to Liferay at http://localhost:8080. Use the email address test@liferay.com and the password test. When prompted, change the password to learn.
Then, follow these steps:
-
Download and unzip User Account API Basics.
curl https://resources.learn.liferay.com/dxp/latest/en/users-and-permissions/developer-guide/liferay-y6q4.zip -Ounzip liferay-y6q4.zip -
Use the cURL script to add a new User to your Liferay instance. On the command line, navigate to the
curlfolder. Execute theUser_POST_ToInstance.shscript../User_POST_ToInstance.shThe JSON response shows a new user has been added:
{ "additionalName": "", "alternateName": "able", "birthDate": "1977-01-01T00:00:00Z", "customFields": [], "dashboardURL": "", "dateCreated": "2021-05-19T16:04:46Z", "dateModified": "2021-05-19T16:04:46Z", "emailAddress": "able@liferay.com", "familyName": "Foo", "givenName": "Able", "id": 39321, "jobTitle": "", "keywords": [], "name": "Able Foo", "organizationBriefs": [], "profileURL": "", "roleBriefs": [ { "id": 20113, "name": "User" } ], "siteBriefs": [ { "id": 20127, "name": "Global" }, { "id": 20125, "name": "Guest" } ], "userAccountContactInformation": { "emailAddresses": [], "facebook": "", "jabber": "", "postalAddresses": [], "skype": "", "sms": "", "telephones": [], "twitter": "", "webUrls": [] } }%Open the Global Menu (
 ) and navigate to Control Panel → Users and Organizations. Verify the addition of a new user. Note the user’s
) and navigate to Control Panel → Users and Organizations. Verify the addition of a new user. Note the user’s idnumber for later commands.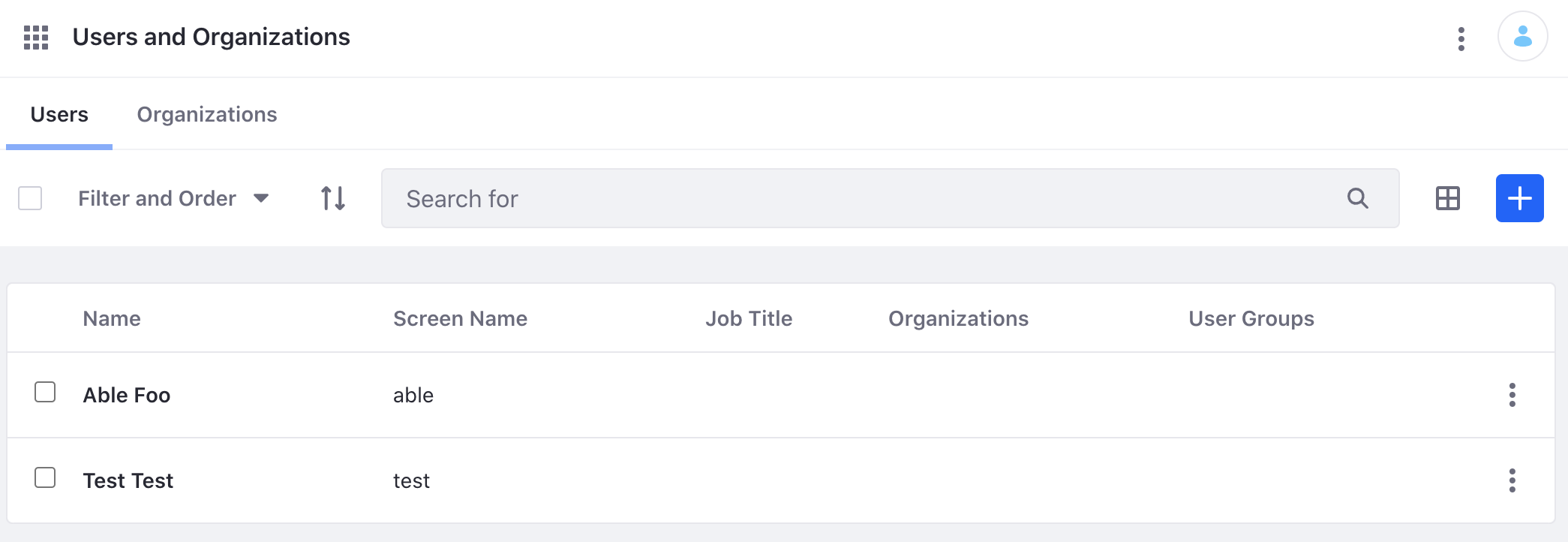
-
The REST service can also be called with a Java class. Navigate out of the
curlfolder and into thejavafolder. Compile the source files with the following command:javac -classpath .:* *.java -
Run the
User_POST_ToInstanceclass with the following command:java -classpath .:* User_POST_ToInstanceOpen the Global Menu (
 ) and navigate to Control Panel → Users and Organizations. Verify the addition of a new user.
) and navigate to Control Panel → Users and Organizations. Verify the addition of a new user.
Read on to see how the cURL command and Java class work.
Examine the cURL Command
The User_POST_ToInstance.sh script calls the REST service with a cURL command.
curl \
"http://localhost:8080/o/headless-admin-user/v1.0/user-accounts" \
--data-raw '
{
"alternateName": "Able",
"emailAddress": "able@liferay.com",
"familyName": "Foo",
"givenName": "Able"
}' \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request "POST" \
--user "test@liferay.com:learn"
Here are the command’s arguments:
| Arguments | Description |
|---|---|
-H "Content-Type: application/json" | Indicates that the request body format is JSON. |
-X POST | The HTTP method to invoke at the specified endpoint |
"http://localhost:8080/o/headless-admin-user/v1.0/user-accounts" | The REST service endpoint |
-d "{\"alternateName\": \"Able\", \"emailAddress\": \"able@liferay.com\", \"familyName\": \"Foo\", \"givenName\": \"Able\"}" | The data you are requesting to post |
-u "test@liferay.com:learn" | Basic authentication credentials |
Basic authentication is used here for demonstration purposes. For production, you should authorize users via OAuth2. See Using OAuth2 to Authorize Users for a sample React application that uses OAuth2.
The other cURL commands use similar JSON arguments.
Examine the Java Class
The User_POST_ToInstance.java class adds a user by calling the user related service.
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
UserAccountResource.Builder builder = UserAccountResource.builder();
UserAccountResource userAccountResource = builder.authentication(
"test@liferay.com", "learn"
).build();
UserAccount userAccount = userAccountResource.postUserAccount(
new UserAccount() {
{
alternateName = "Baker";
emailAddress = "baker@liferay.com";
familyName = "Foo";
givenName = "Baker";
}
});
System.out.println(userAccount);
}
The class calls the REST service with only three lines of code:
| Line (abbreviated) | Description |
|---|---|
UserAccountResource.Builder builder = ... | Gets a Builder for generating a UserAccountResource service instance. |
UserAccountResource userAccountResource = builder.authentication(...).build() | Specifies basic authentication and generates a UserAccountResources service instance. |
UserAccount userAccount = userAccountResource.postUserAccount(...) | Calls the userAccountResource.postUserAccount method and passes the data to post. |
Note that the project includes the com.liferay.headless.admin.user.client.jar file as a dependency. You can find client JAR dependency information for all REST applications in the API explorer in your installation at /o/api.
The main method’s comment demonstrates running the class.
The other example Java classes are similar to this one but call different UserAccountResource methods.
See UserAccountResource for service details.
Below are examples of calling the other user REST services using cURL and Java.
Get Instance Users
Get a list of all users with the following cURL and Java commands.
Users_GET_FromInstance.sh
Command:
./Users_GET_FromInstance.sh
Code:
curl \
"http://localhost:8080/o/headless-admin-user/v1.0/user-accounts" \
--user "test@liferay.com:learn"
Users_GET_FromInstance.java
Command:
java -classpath .:* Users_GET_FromInstance
Code:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
UserAccountResource.Builder builder = UserAccountResource.builder();
UserAccountResource userAccountResource = builder.authentication(
"test@liferay.com", "learn"
).build();
Page<UserAccount> page = userAccountResource.getUserAccountsPage(
null, null, Pagination.of(1, 2), null);
System.out.println(page);
}
All the users from your instance appear in the JSON response.
Filtering, Paginating, Searching, and Sorting Orders
Users returned by this API can be filtered, paginated, searched, and sorted. See the getUserAccountsPage method for more information. Use the following UserAccount fields to filter, search, and sort the results:
keywordsroleNamesuserGroupRoleNamesbirthDatedateCreateddateModifiedlastLoginDateorganizationIdsroleIdsuserGroupIds- Liferay DXP 2024.Q3+/Portal 7.4 GA125+
status alternateNamescreenNameemailAddressfamilyNamegivenNamejobTitlename- Liferay DXP 2024.Q4+/Portal 7.4 GA129+
customFields
| Filter Query | Description |
|---|---|
status eq 0 | The user account status must be Active. |
status eq 5 | The user account status must be Inactive. |
roleIds in ('20100', 20104') | The user account must have the role of an Administrator (20100) or a Power User (20104). |
jobTitle eq 'Parts Consultant' | The user account job title must be Parts Consultant. |
customFields/githubProfileUrl eq 'www.github.com/able.foo' | The user account has a custom field called githubProfileUrl with the value www.github.com/able.foo. |
| Sort Query | Description |
|---|---|
dateCreated:desc | Sort by dateCreated in descending order. |
dateCreated:desc,lastLoginDate:desc | Sort by dateCreated in descending order first, then by lastLoginDate in descending order. |
Read API Query Parameters for more information.
Get a User
Get a specific user with the following cURL and Java commands. Note, replace 1234 with your user’s ID.
User_GET_ById.sh
Command:
./User_GET_ById.sh 1234
Code:
curl \
"http://localhost:8080/o/headless-admin-user/v1.0/user-accounts/${1}" \
--user "test@liferay.com:learn"
User_GET_ById.java
Command:
java -classpath .:* -DuserId=1234 User_GET_ById
Code:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
UserAccountResource.Builder builder = UserAccountResource.builder();
UserAccountResource userAccountResource = builder.authentication(
"test@liferay.com", "learn"
).build();
System.out.println(
userAccountResource.getUserAccount(
Long.valueOf(System.getProperty("userId"))));
}
The user is returned in the JSON response.
Patch a User
Do a partial edit of an existing user with the following cURL and Java commands. Note, replace 1234 with your user’s ID.
User_PATCH_ById.sh
Command:
./User_PATCH_ById.sh 1234
Code:
curl \
"http://localhost:8080/o/headless-admin-user/v1.0/user-accounts/${1}" \
--data-raw '
{
"familyName": "Bar"
}' \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request "PATCH" \
--user "test@liferay.com:learn"
User_PATCH_ById.java
Command:
java -classpath .:* -DuserId=1234 User_PATCH_ById
Code:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
UserAccountResource.Builder builder = UserAccountResource.builder();
UserAccountResource userAccountResource = builder.authentication(
"test@liferay.com", "learn"
).build();
UserAccount userAccount = userAccountResource.patchUserAccount(
Long.valueOf(System.getProperty("userId")),
new UserAccount() {
{
familyName = "Bar";
}
});
System.out.println(userAccount);
}
In the example, Able and Baker’s last names have changed from Foo to Bar.
Put a User
Do a complete overwrite of an existing user with the following cURL and Java commands. Note, replace 1234 with your user’s ID.
User_PUT_ById.sh
Command:
./User_PUT_ById.sh 1234
Code:
curl \
"http://localhost:8080/o/headless-admin-user/v1.0/user-accounts/${1}" \
--data-raw '
{
"alternateName": "Able",
"emailAddress": "able@liferay.com",
"familyName": "Goo",
"givenName": "Able"
}' \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request "PUT" \
--user "test@liferay.com:learn"
User_PUT_ById.java
Command:
java -classpath .:* -DuserId=1234 User_PUT_ById
Code:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
UserAccountResource.Builder builder = UserAccountResource.builder();
UserAccountResource userAccountResource = builder.authentication(
"test@liferay.com", "learn"
).build();
UserAccount userAccount = userAccountResource.putUserAccount(
Long.valueOf(System.getProperty("userId")),
new UserAccount() {
{
alternateName = "Baker";
emailAddress = "baker@liferay.com";
familyName = "Goo";
givenName = "Baker";
}
});
System.out.println(userAccount);
}
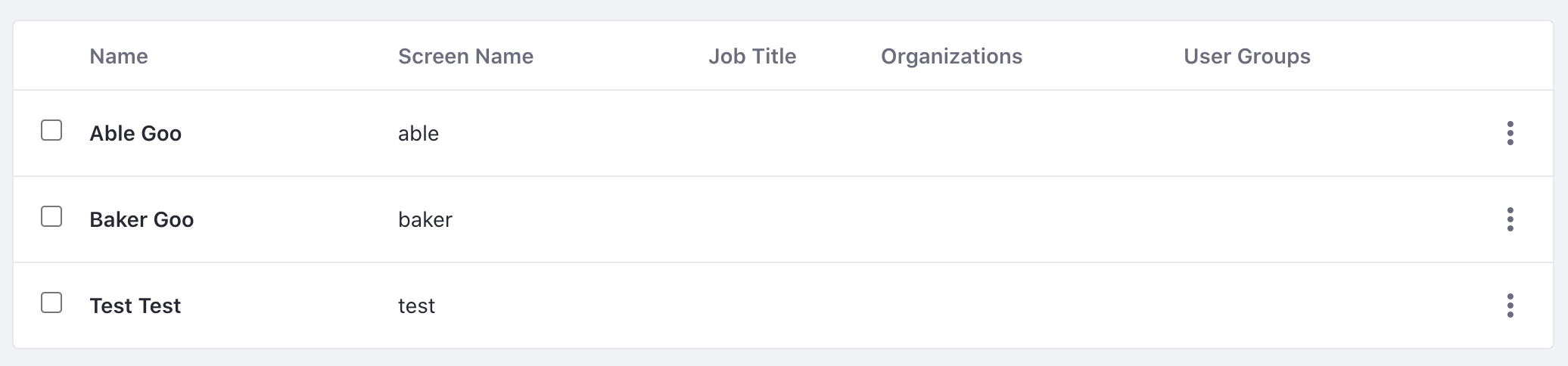
This replaces the previous data with Able Goo and Baker Goo in the example.
Use User_PATCH_ById.[java|sh] or User_PUT_ById.[java|sh] to activate or deactivate a user by changing the status field to Active or Inactive.
To change the status of a user with a workflow active, you must use the headless-admin-workflow API instead. Find usage details in the API Explorer.
Delete a User
Delete an existing user with the following cURL and Java commands. Note, replace 1234 with your user’s ID.
User_DELETE_ById.sh
Command:
./User_DELETE_ById.sh 1234
Code:
curl \
"http://localhost:8080/o/headless-admin-user/v1.0/user-accounts/${1}" \
--request "DELETE" \
--user "test@liferay.com:learn"
User_DELETE_ById.java
Command:
java -classpath .:* -DuserId=1234 User_DELETE_ById
Code:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
UserAccountResource.Builder builder = UserAccountResource.builder();
UserAccountResource userAccountResource = builder.authentication(
"test@liferay.com", "learn"
).build();
userAccountResource.deleteUserAccount(
Long.valueOf(System.getProperty("userId")));
}
This deletes both users Able Goo and Baker Goo.
Related Topics
Check out the API Explorer to see the list of all User related REST services.
Get user postal addresses with PostalAddresses_GET_FromUser